Most Product Managers have relatively narrow roles and decision rights on product portfolios are fragmented on various functions. This creates  incoherence between a company’s product and its overall Corporate Strategy.
incoherence between a company’s product and its overall Corporate Strategy.
What is needed is more accountable decision rights that align responsibility for results to one person who also has cross-functional decision-making authority. This realignment is at the core of Strong-form Product Management.
What is Product Management
Product Management is an organizational lifecycle function within a company. Product Management deals with the planning, forecasting, production, and marketing of the product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle.
The Product Life Cycle (PLM) Management integrates people, data, processes, and business systems. It provides product information for companies and their extended supply chain enterprise. One of the ultimate goals of Product Management is to optimize the business at the product, product line or product portfolio level over the lifecycle of the products.
Taking a Cautionary Case in Point: Understanding What Happened to Research in Motion (RIM)
In April 2007, Research in Motion (RIM) was flying high. The Blackberry creator was coming off its best year ever. RIM was experiencing record revenues, record earnings per share, and record shipments. And there was a new reason to be optimistic: Apple had just introduced the iPhone and RIM executives took it for granted that their product—a runaway hit in the business world—would grab a huge share of the burgeoning consumer market as well.
However, the confidence proved to be ill-founded. The iPhone reversed the historical pattern of computer technologies flowing from the enterprise to the consumer market.
RIM is compelling as a cautionary tale but it is not unique. Many companies falter in the face of discontinuous change. Their failure usually stems from their inability to keep up with technological shifts or the complexity of their product lines. Though often seen as a breakdown at the enterprise level, this starts at a much more granular level, with ineffective Product Management.
A Strong-form Model could have kept RIM stay ahead of change and remain competitive.
The Strong-form Product Management Model
The 5 steps to Strong-form Product Management will keep competition at bay.
- Hire Product Managers with Proper Skills
We need to understand that intrinsic abilities are required by Product Managers. These are the abilities to make a judgment to understand trade-offs, anticipate market changes, and make savvy business decisions. - Create Financial Transparency to the Product Level
Companies must realize that a given product may be siphoning revenue from more profitable products. Increase in costs from suppliers that are managed by another function may cause hidden opportunity costs or out-and-out profit surprises. The creation of Financial Transparency down to the product level can address these concerns. - Implement Product-first Decision-making Processes
There is a need to broaden decision rights and increasing accountability of Product Managers for performance and results. Product Managers have a “first among equals” status. - Develop Strong Customer Relations
Product Manager must translate customer insights into product improvement and new products. - Encourage Cross-functional Collaboration
Strong-form Product Management is inherently cross-functional. Communication is essential in developing the relationships between marketing and product management.
In all these steps, the Strong-form Product Manager must be the center of knowledge. However, Product Managers must also realize that the adoption of a Strong-form Product Management Approach requires taking Change Management initiatives.
Undertaking a Change Management initiative can take years to implement. Success can be achieved when anchored on basic principles of Change Management. However, once this is put in place, significant opportunities arise as companies move from strategy to execution.
Interested in gaining more understanding of the Strong-form Product Management Model? You can learn more and download an editable PowerPoint about Strong-form Product Management Model here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Are you a management consultant?
You can download this and hundreds of other consulting frameworks and consulting training guides from the FlevyPro library.



 global economics. Propelled by fast growth in the emerging world, the share of family businesses in the global Fortune 500 grew from 15% in 2005 to 19% in 2013. Five years ago, founders or their families owned 60% of emerging-market companies with sales of $1 billion or more. By 2025, an additional 4,000 companies may join the list. Family-owned businesses would represent 40% of the world’s large enterprise.
global economics. Propelled by fast growth in the emerging world, the share of family businesses in the global Fortune 500 grew from 15% in 2005 to 19% in 2013. Five years ago, founders or their families owned 60% of emerging-market companies with sales of $1 billion or more. By 2025, an additional 4,000 companies may join the list. Family-owned businesses would represent 40% of the world’s large enterprise.

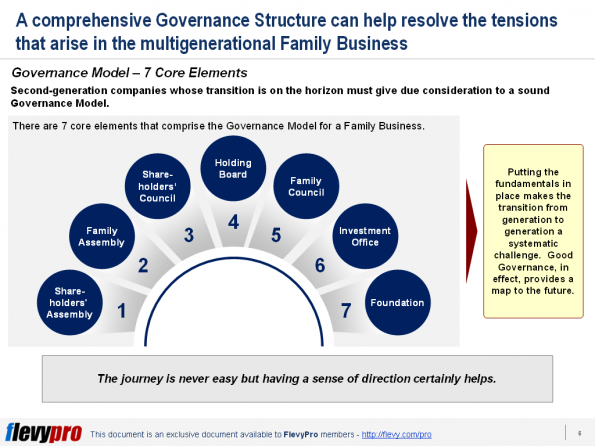
 generation. Establishing a set of Councils and Boards is essential in addressing critical transition issues. With a Governance Model,
generation. Establishing a set of Councils and Boards is essential in addressing critical transition issues. With a Governance Model,