The pressure on Boards and Directors to raise their game has remained acute. A survey of more than 770 directors from public and private  companies across the industries around the world suggested that some are responding more energetically than others.
companies across the industries around the world suggested that some are responding more energetically than others.
There is a dramatic difference between how directors allocate their time among boardroom activities and the effectiveness of the Boards. One in four directors assessed their impact as moderate or lower, while others reported as having a high impact across Board functions.
Today, the call to become more forward-looking and achieving Board Excellence is further highlighted. This is further emphasized when the Board and Management are pressured to find the best answers to global business concerns and issues. In Strategy Development, this becomes invaluable. It does not only lead to clearer strategies but also the creation of alignment essential in making bolder moves.
While these are essential, there is a need to raise the quality of engagement on strategy between the Board and Management for each group to achieve smarter options. This is possible only if organizations have high impact, strategic Boards in place.
High impact, strategic Boards have a greater impact as they move beyond the basics and face increasing challenges.
The Challenges that Today’s Board Face
Business is fast-changing and rapidly transforming. The global economy is increasingly pushing businesses, as well as the Board to face a gamut of challenges.
What are the 2 main challenges facing Boards today?
First is Time Commitment. Working at a high level takes discipline – and time. In fact, the greater time commitment is expected on high impact activities. The Board often have 6 to 8 meetings a year. As a result, they are often hard-pressed to get beyond the compliance-related topics to secure the breathing space needed for developing a strategy.
Often, it is the very high impact Directors who invest more time compared to moderate or lower average Directors.
Who are your very high impact Directors? They are those spend a total of 40 days a year working for the Board compared to 19 days of low impact Directors. An extra 8 workdays a year is invested in strategy and an extra 3 workdays a year are spent on Performance Management, M&A, Organizational Health, and Risk Management.
High impact Directors who believe that their activities have greater impact spend significantly more time on these activities compared to low impact Boards.
Second is Strategy Understanding. Why is Strategy Understanding a challenge for the Board? Limited understanding of the organization’s strategy can result in the Board’s limited engagement with the organization. Based on the survey made, only 21% of the Directors have a complete understanding of the current strategy. Often, Board members have a better understanding of the company’s financial position rather than its risks or industry dynamics.
If we look at high impact Directors, they invest more time in dealing with strategic issues. In fact, they invest 8 extra workdays a year on Strategic Planning and discussing strategy compared to low impact Directors. High impact Directors center on Strategy Focus Areas which can, in turn, spur high-quality engagement from the Board on strategy development. The quality of Board engagement on strategy is enhanced, both when the engagement is deep and during the regular course of business.
The Board just needs to focus on 3 areas of discussion for the Board to enhance Strategy Development. One of them is Industry and Competitive Dynamics.
Interested in gaining more understanding of Board Excellence via High Impact, Strategic Boards? You can learn more and download an editable PowerPoint about Board Excellence: High Impact, Strategic Boards here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Are you a management consultant?
You can download this and hundreds of other consulting frameworks and consulting training guides from the FlevyPro library.


 more effective. They want to deliver great customer experience, take advantage of new technologies to cut costs, improve quality and transparency, and build value.
more effective. They want to deliver great customer experience, take advantage of new technologies to cut costs, improve quality and transparency, and build value.
 Digital Age has increased both the opportunities for businesses who know how to react and the difficulty of getting it right.
Digital Age has increased both the opportunities for businesses who know how to react and the difficulty of getting it right.
 good attitude, and a solid work ethic. Members of the team get along well with each other. When you put all these together, you get to achieve results. The team gets to deliver high-quality projects on time and to spec.
good attitude, and a solid work ethic. Members of the team get along well with each other. When you put all these together, you get to achieve results. The team gets to deliver high-quality projects on time and to spec.
 organization’s mission and reduce costs. In all too many companies, reengineering has been not only a great success but also a great failure. After months, even years, of a careful redesign, these companies achieve dramatic improvements in individual processes only to watch overall results decline.
organization’s mission and reduce costs. In all too many companies, reengineering has been not only a great success but also a great failure. After months, even years, of a careful redesign, these companies achieve dramatic improvements in individual processes only to watch overall results decline.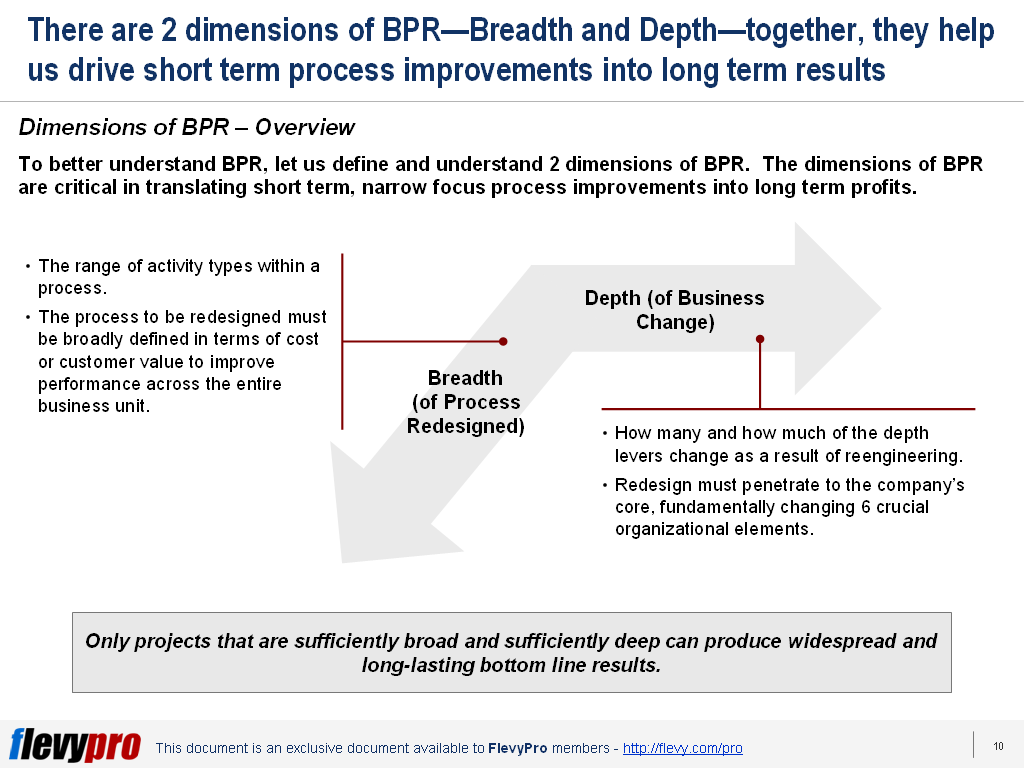
 becoming more demanding and accustomed to getting what they want.
becoming more demanding and accustomed to getting what they want.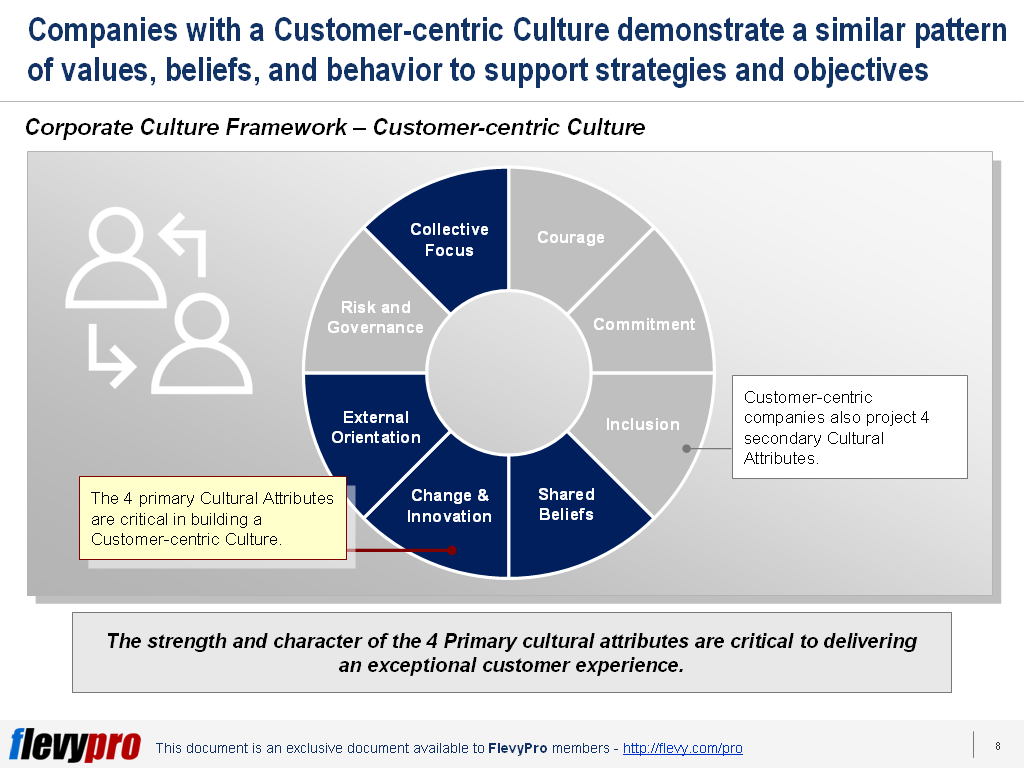
 Loyalty
Loyalty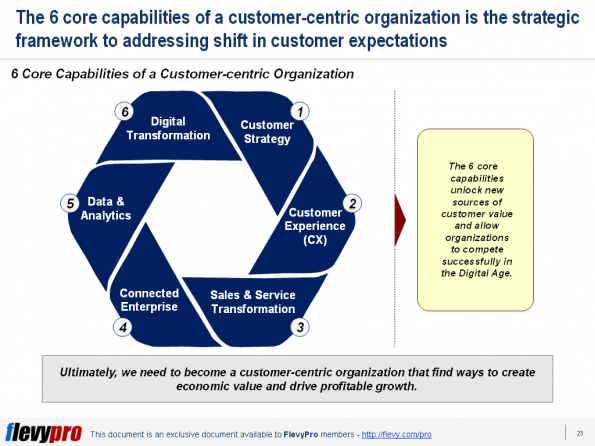
 data analytics is now a quintessential business matter. It is important for CEOs and top executives to be able to clearly articulate its purpose and translate it into action. Yet, this is not so.
data analytics is now a quintessential business matter. It is important for CEOs and top executives to be able to clearly articulate its purpose and translate it into action. Yet, this is not so.
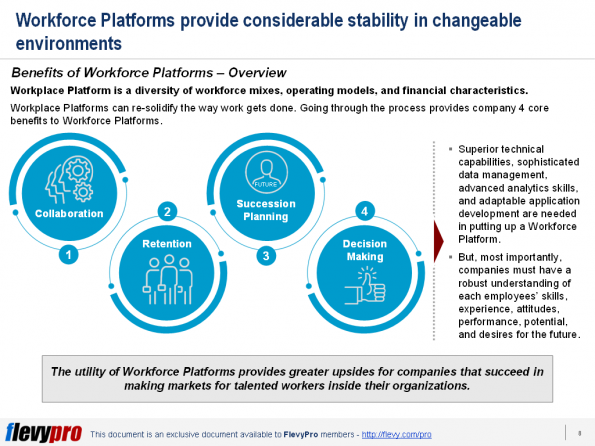
 digital technology into the labor force which can threaten to destabilize crucial aspects of how employees work by. This can undermine the stability companies depend on to be agile.
digital technology into the labor force which can threaten to destabilize crucial aspects of how employees work by. This can undermine the stability companies depend on to be agile.