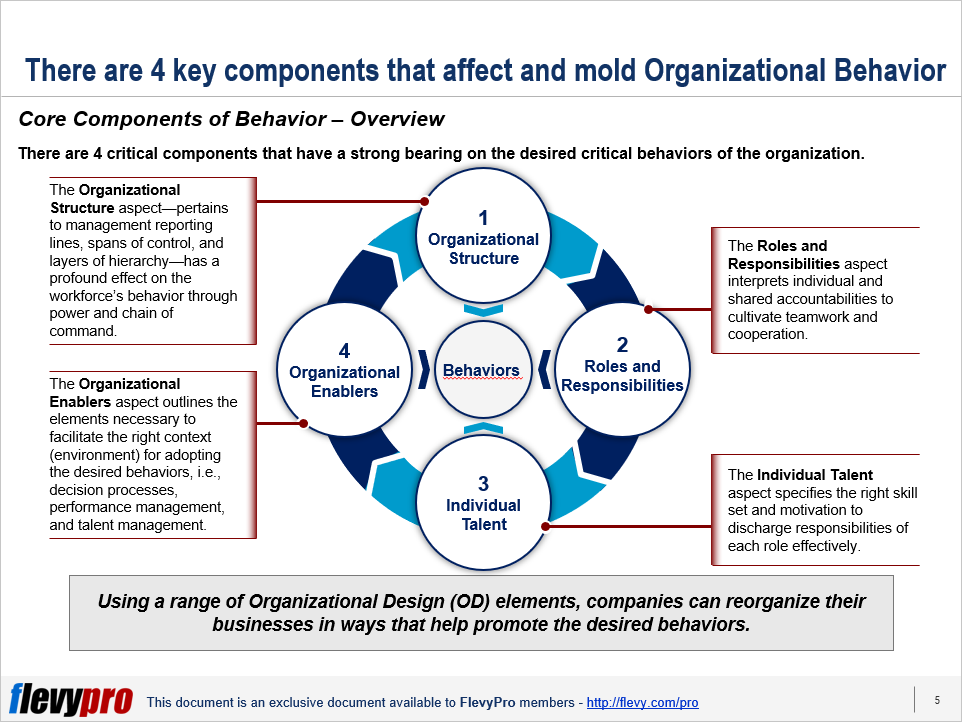
Inculcating productive workforce behaviors is of utmost significance in Business Transformation, successful Strategy Execution, and Performance Improvement. However, making people embrace productive behaviors involves a concerted effort across the organization.
Inculcating productive workforce behaviors is of utmost significance in Business Transformation, successful Strategy Execution, and Performance Improvement. However, making people embrace productive behaviors involves a concerted effort across the organization.
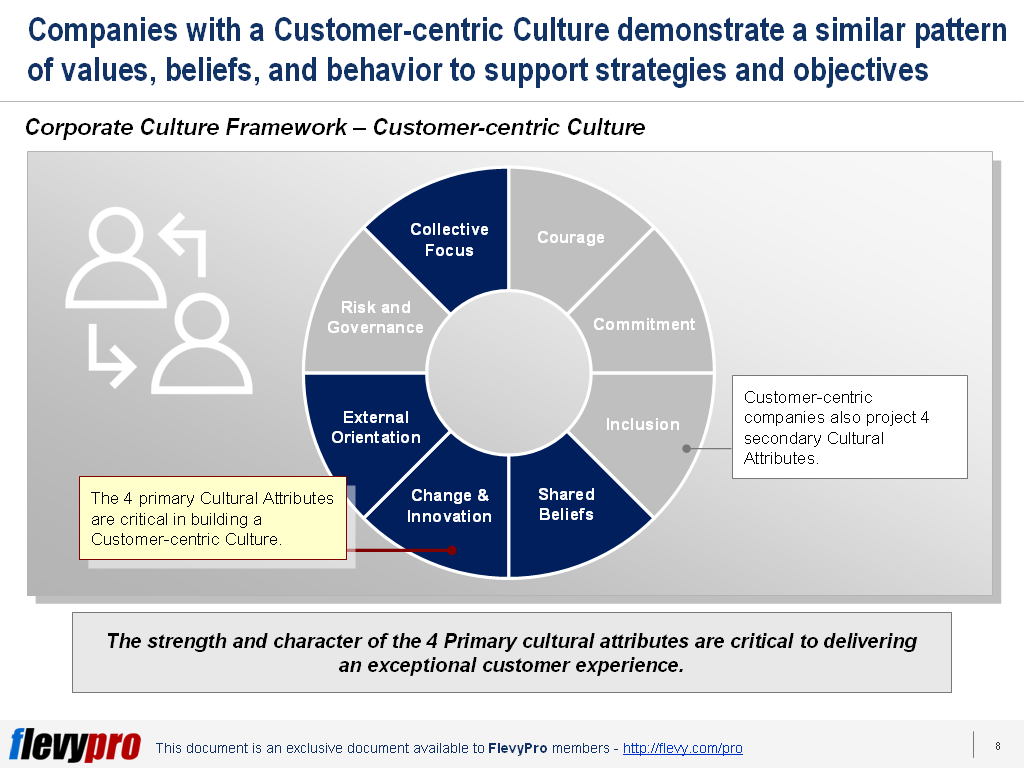
The realization of Transformation, Strategy, and Performance improvement goals can become a reality by developing a thorough understanding of the 4 components of Organizational Behavior. These components act as powerful levers in shaping the desired behaviors in the workforce:
- Organizational Structure
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Individual Talent
- Organizational Enablers
These Organizational Design levers work effectively when combined and aligned. Let’s discuss the first 2 levers in detail now.
Organizational Structure
Organizational Structure represents the management reporting lines that create the organization’s spans of control, layers, and number of resources. Organizational Structure is a foundational driver to Organizational Design, which also has a strong positive bearing on promoting the behaviors critical to improve the overall performance of the enterprise. This is owing to the power that a position exerts on the subordinates based on factors that are important for individuals—e.g., work, compensation, and career ladder.
The Organizational Structure indicates an enterprise’s priorities. An organization is typically structured in accordance with its top most priority. For instance, functional organizational structure is adopted by enterprises having functional excellence as a priority. In present-day’s competitive markets, most organizations have to deal with several priorities at a given time, which could be conflicting. However, this does not mean adding new structures on top of existing ones, thereby increasing unnecessary complexity. Creating overly complex structures to manage multiple priorities results in red tape and delayed decisions. All roles are interdependent, necessitating cooperation. This means taking care of the needs of others—instead of just watching over personal priorities—and encouraging individual behaviors that boost the efficiency of groups to achieve collective objectives.
Roles & Responsibilities
Roles and responsibilities deal with tasks allocated to each position and individual. Organizational Design depends heavily on redefining clearer and compelling roles and responsibilities—to avoid any duplication of efforts or creating adversaries among team members. In a collaborative culture where cooperation is the mainstay of an organization, individuals should not only be aware of what is required of them, but also appreciate the responsibilities of their team members, the authorities their roles exercise, the skills required, and the metrics to measure success.
A methodical way to outline roles and responsibilities effectively—while minimizing complexity—that encourages cooperation and empowerment is through the “Role Chartering” technique. The technique requires distinctly identifying all roles on the basis of 6 key factors:
- Describing shared and individual accountabilities
- Outlining indicators to track success
- Specifying who has the right to decide what
- Indicating the capabilities critical for roles
- Assigning the leadership traits valuable for the roles
- Charting the abilities required for accomplishing personal and team goals.
Interested in learning more about these components to Organizational Behavior? You can download an editable PowerPoint on Organizational Behaviors here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Are you a Management Consultant?
You can download this and hundreds of other consulting frameworks and consulting training guides from the FlevyPro library.

 intensifies. This often happens when the Board spends more time looking in the rearview mirror and not enough scanning the road ahead. When this happens, governance suffers.
intensifies. This often happens when the Board spends more time looking in the rearview mirror and not enough scanning the road ahead. When this happens, governance suffers.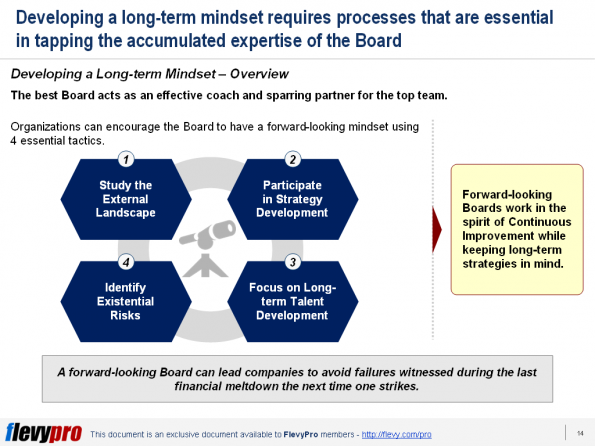
 companies across the industries around the world suggested that some are responding more energetically than others.
companies across the industries around the world suggested that some are responding more energetically than others.


 Business dashboards
Business dashboards
 more effective. They want to deliver great customer experience, take advantage of new technologies to cut costs, improve quality and transparency, and build value.
more effective. They want to deliver great customer experience, take advantage of new technologies to cut costs, improve quality and transparency, and build value.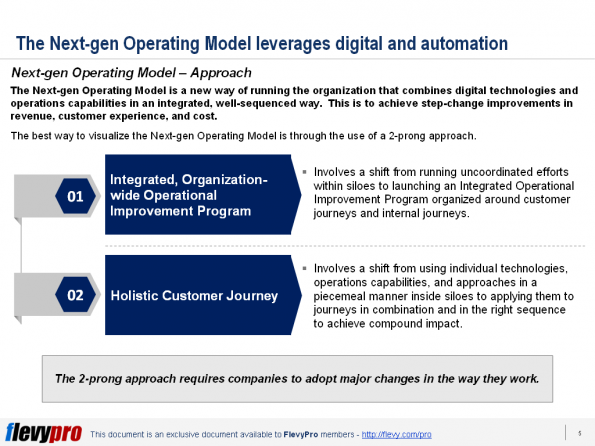
 Digital Age has increased both the opportunities for businesses who know how to react and the difficulty of getting it right.
Digital Age has increased both the opportunities for businesses who know how to react and the difficulty of getting it right.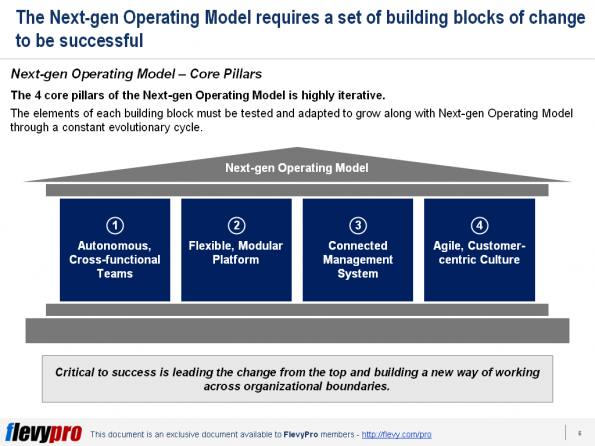
 good attitude, and a solid work ethic. Members of the team get along well with each other. When you put all these together, you get to achieve results. The team gets to deliver high-quality projects on time and to spec.
good attitude, and a solid work ethic. Members of the team get along well with each other. When you put all these together, you get to achieve results. The team gets to deliver high-quality projects on time and to spec.
 organization’s mission and reduce costs. In all too many companies, reengineering has been not only a great success but also a great failure. After months, even years, of a careful redesign, these companies achieve dramatic improvements in individual processes only to watch overall results decline.
organization’s mission and reduce costs. In all too many companies, reengineering has been not only a great success but also a great failure. After months, even years, of a careful redesign, these companies achieve dramatic improvements in individual processes only to watch overall results decline.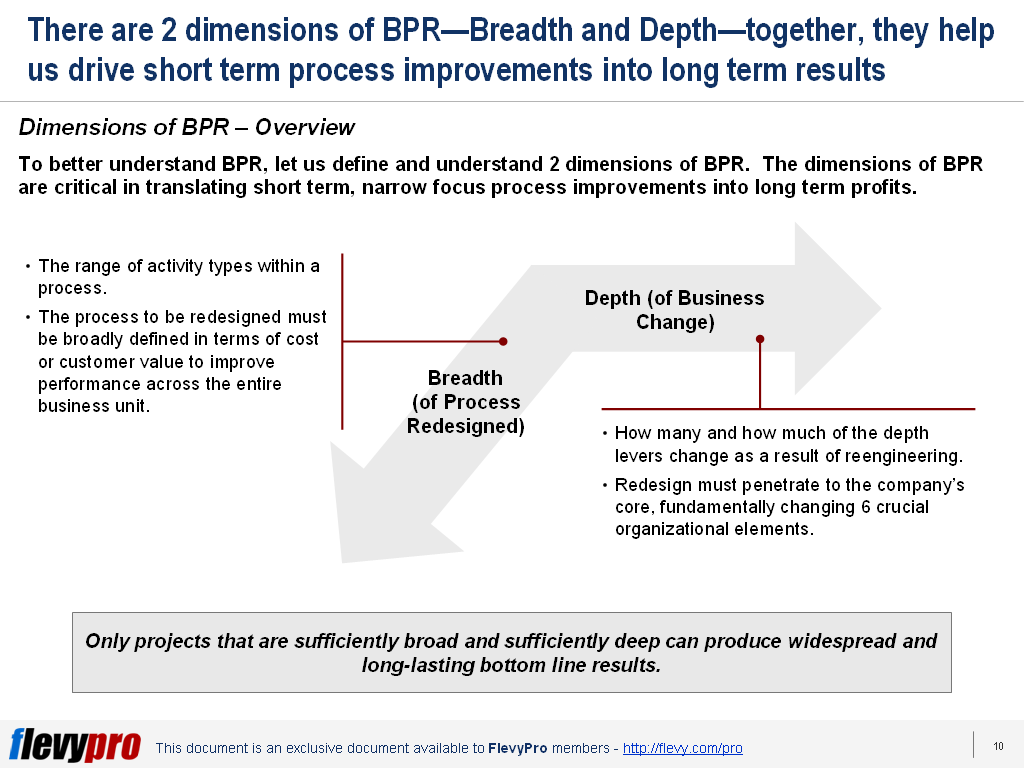
 becoming more demanding and accustomed to getting what they want.
becoming more demanding and accustomed to getting what they want.